Our world is full of physical objects embedded with technologies that connect and exchange data. Our journal dedicated to Internet of Things provides an environment for crystallizing original results and achievements in this domain. Its scope encompasses all areas related to the technologies and related application fields. In this article, we present 5 research articles from this journal, that are fully accessible for free in our EUDL open library.
1 Smart Helmet Design for Potholes and Air Pollution Monitoring
In a country with an extensive road network, it is very tough for authorities to identify and repair the potholes on time, which emerge due to casual wear and tear of the road. These potholes are dangerous for unsuspecting high-speed vehicles and results in multiple life-threatening accidents year-round.
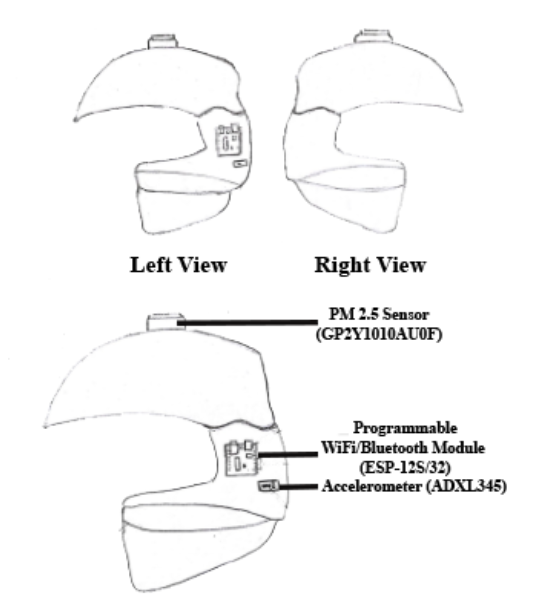
Apart from potholes, another severe concern about the time spent on roads is air pollution. Breathing the polluted air, mainly containing the particulate matter that has a diameter of fewer than 2.5 micrometers, is toxic to humans.
In this work, the authors Vibhutesh Kumar Singh, Himanshu Chandna (Indraprastha Institute of Information Technology), and Nidhi Upadhyay (Circuit Uncle™) have judiciously designed an Internet of Things based smart helmet, which uses crowdsourcing to report potholes and collect crucial on-road air pollution data so that a person could avoid risk to life and health. They have also introduced the novel concept of remembrance factor and severity index, which could be useful in dealing with the stale and invalid pothole data in the database. SmartPPM: An Internet of Things Based Smart Helmet Design for Potholes and Air Pollution Monitoring appears in issue 18 of EAI endorsed transactions on the Internet of Things journal.
2 Network That Delivers Reliable Performance 24 Hours a Day 7 Days a Week for Higher Education in Uganda
The work of Yakubu Ajiji Makeri (Kampala International University Uganda) aims at existing defects of traditional VPN (Virtual Private Network) in constructing enterprise network, analyses problems which must be considered in designing secure enterprise network, puts forward solution of DMVPN (Dynamic Multipoint VPN) technique to solve the problems that traditional VPN has not solved by now.
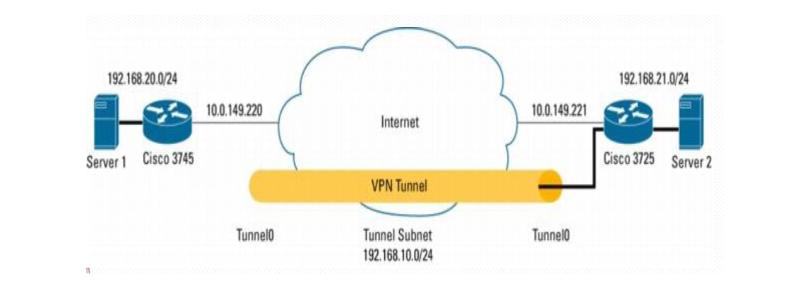
At the same time, it expatiates on the implementation mechanism of DMVPN, puts forward a concrete case that to adopts the DMVPN technique constructs secure enterprise network of some universities and business chain organization, and network performance indexes are tested.
From the results of the test, the DMVPN network entirely satisfies the actual requirements that an enterprise uses a network. It offers a mode that is a convenient and economical investment to an enterprise for building a secure network. To Design a Network That Delivers Reliable Performance 24 Hours a Day 7 Days a Week for Higher Education in Uganda appears in issue 22 of EAI endorsed transactions on the Internet of Things journal.
3 Improving the Security of Internet of Things with Limited Resources
This research from the authors Abdul Hannan Khan, Shahan Yamin Siddiqui (School of Computer Science, National College of Business Administration & Economics), Muhammad Sohail Irshad, Saif Ali (Department of Computer Science, Minhaj University), Muhammad Rehan Saleem (Department of Computer Science, University of Management and Technology), and Shahid Iqbal (Department of Computer Science & IT, Virtual University of Pakistan) is about the information security of very obliged gadgets.
Design Science Research (DSR) Method is utilized for this reason. It let the authors pick up the fundamental thought and exploration of the primary issue space. This is a procedure of combining distinctive pre-affirmed examines to pick up the goal. Symmetric cryptography will be utilized as a noteworthy device in various information items and entryway gadgets.
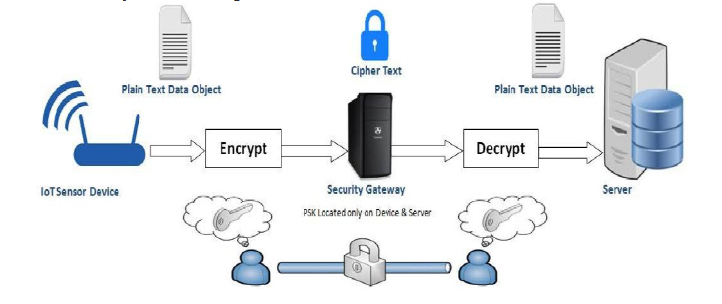
The principle target of this exploration is to give security to exceptionally constrained gadgets as they are not ready to convey utilizing TLS or DTLS given a deficiency of assets. This arrangement is a finished bundle to give credibility, information honesty and privacy, either information is making a trip to entryway, gadgets or the web. At the information interface layer, AES symmetric encryption is utilized and information questions likewise are encoded utilizing a similar encryption strategy. Assessment is performed using wire shark. Analytical Method to Improve the Security of Internet of Things with Limited Resources appears in Issue 18 of EAI endorsed transactions on the Internet of Things journal.
4 IoT-Q-Band: A low cost internet of things based wearable band to detect and track absconding COVID-19 quarantine subjects
The world health organization (WHO) has declared the novel coronavirus disease (nCoV or COVID-19) outbreak a pandemic, and quarantines are playing a vital role in containing its spread. But globally, the defections of the quarantined subjects are raising serious concerns. If COVID-19 positive, the absconding quarantine subjects can infect more people, which makes the timely detection of them vital.
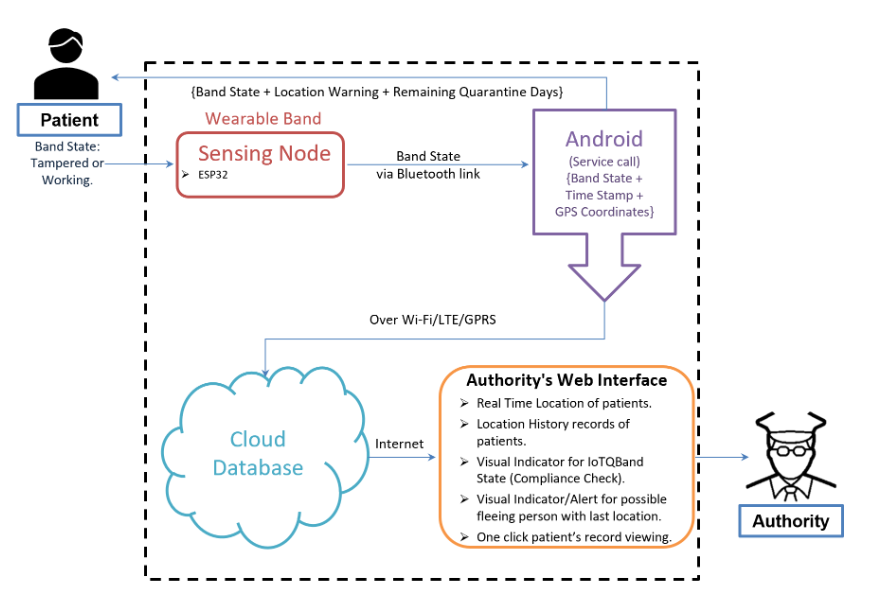
As the literature suggests, a wearable makes a subject more compliant towards healthcare routines/restrictions. In this work, the authors Vibhutesh Kumar Singh, Himanshu Chandna, Ashish Kumar, Sujeet Kumar, Nidhi Upadhyay, and Kumar Utkarsh have designed an IoT based wearable quarantine band (IoT-Q-Band) to detect the absconding. While designing it, we kept in mind the cost, global supply chain disruption, and COVID-19 quarantine duration, which the WHO recommends. This wearable prototype, with the bundled mobile app, reports and tracks the absconding quarantine subjects in real-time. IoT-Q-Band is an economical solution that could benefit low-income regions to prevent the spread of COVID-19. IoT-Q-Band: A low-cost internet of things based wearable band to detect and track absconding COVID-19 quarantine subjects appears in issue 20 of EAI endorsed transactions on the Internet of Things journal.
5 IoT Short-range Network protocols: Analytical study and operating models
According to the authors of this paper Sakina Elhadi, Abdelaziz Marzak, Nawal Sael (University Hassan II Casablanca), Internet of Things (IoT) is a constantly evolving concept. Nonetheless, we can consider that the Internet of Things broadly refers to the trend towards generalized interconnection of all the objects that surround our daily lives, places and physical environments. Among the success keys of Iot there are protocols. However, the lack of a single connectivity protocol causes a lack of interoperability between IoT devices and applications.
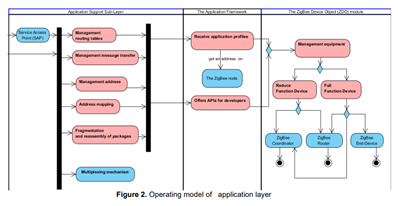
In this article, authors present a detailed comparative study of the Short-range network protocols and the operating models of these protocols. There models facilitates the in-depth understanding of how network protocols work. Subsequently, from the comparative study already established and these proposed models authors determine the priority of the criteria of these protocols. Using the projection of these criteria on the proposed operating models. This will help to choose the adaptable protocol for a type of IoT applications. IoT Short-range Network protocols: Analytical study and operating models appears in issue 25 of EAI endorsed transactions on the Internet of Things journal.
Subscribe to our Internet of Things journal and never miss new content in your field of research.

