To be aware of the growing threats in internet security, we have to understand the complexity of network and service infrastructures. We also need technology to enable network security monitoring and tracing, to assess the trustworthiness of infrastructures and services.
EAI Endorsed Transactions on Security and Safety publishes research articles, reviews, commentaries, editorials, technical articles, and short communications. In this blog, we present top 5 research articles from it, that are fully accessible for free in our EUDL open library.
1 A Deep Learning Approach for Network Intrusion Detection System
A Network Intrusion Detection System (NIDS) helps system administrators to detect network security breaches in their organizations. However, many challenges arise while developing a flexible and efficient NIDS for unforeseen and unpredictable attacks.
Authors of this research article – Quamar Niyaz, Weiqing Sun, Ahmad Y Javaid, and Mansoor Alam (all from the University of Toledo) proposed a deep learning-based approach for developing an efficient and flexible NIDS. A sparse autoencoder and soft-max regression-based NIDS was implemented.
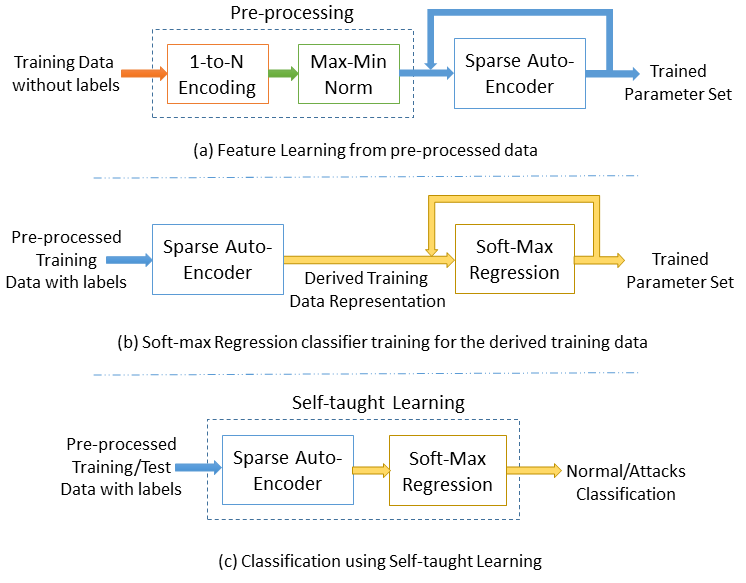
A Deep Learning Approach for Network Intrusion Detection System appeared in issue 9 of EAI endorsed transactions on Security and Safety journal.
2 Do Metadata-based Deleted-File-Recovery (DFR) Tools Meet NIST Guidelines?
Digital forensics (DF) tools are used for the post-mortem investigation of cyber-crimes. CFTT (Computer Forensics Tool Testing) program at the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) has defined expectations for a digital forensics tool’s behavior. Understanding these expectations and how DF tools work is critical for ensuring the integrity of the forensic analysis results. In this paper, researchers considered standardization of one class of DF tools which are for Deleted File Recovery (DFR).
Authors Andrew Meyer, and Sankardas Roy designed a list of canonical test file system images to evaluate a DFR tool. Via extensive experiments, they found that many popular DFR tools do not satisfy some of the standards, and compiled a comparative analysis of these tools, which could help the user choose the right tool. Their findings are likely to trigger more research on compliance of standards from the researcher community as well as the practitioners.
Do Metadata-based Deleted-File-Recovery (DFR) Tools Meet NIST Guidelines? research article appeared in issue 21of EAI endorsed transactions on Security and Safety journal.

3 Manipulating Users’ Trust on Amazon Echo: Compromising Smart Home from Outside
Nowadays, voice control becomes a popular application that allows people to communicate with their devices more conveniently. Amazon Echo, designed around Alexa, is capable of controlling devices, e.g., smart lights, etc. Moreover, with the help of IFTTT (if-this-then-that) service, Amazon Echo’s skillset gets improved significantly. However, people who are enjoying these conveniences may not take security into account. Hence, it becomes important to carefully scrutinize the Echo’s voice control attack surface and the corresponding impacts.
In this paper, the authors Yuxuan Chen, Xuejing Yuan, Aohui Wang, Kai Chen, Shengzhi Zhang, and Heqing Huang proposed MUTAE (Manipulating Users’ Trust on Amazon Echo) attack to remotely compromise Echo’s voice control interface. They have also conducted security analysis and performed taxonomy based on different consequences considering the level of trust that users have placed in Echo. Finally, they also proposed mitigation techniques that protect Echo from MUTAE attack. Manipulating Users’ Trust on Amazon Echo: Compromising Smart Home from Outside appeared on issue 22 of EAI endorsed transactions on Security and Safety journal.

4 Human-Generated and Machine-Generated Ratings of Password Strength: What Do Users Trust More?
Proactive password checkers have been widely used to persuade users to select stronger passwords by providing machine-generated strength ratings of passwords. If such ratings do not match human-generated ratings of human users, there can be a loss of trust in PPCs. In order to study the effectiveness of PPCs, it would be useful to investigate how human users perceive such machine- and human-generated ratings in terms of their trust, which has been rarely studied in the literature.

To fill this gap, the authors of this research article Saeed Ibrahim Alqahtani, Shujun Li, Haiyue Yuan, and Patrice Rusconi reported a large-scale crowdsourcing study with over 1,000 workers. The participants were asked to choose which of the two ratings they trusted more. The passwords were selected based on a survey of over 100 human password experts. The results revealed that participants exhibited four distinct behavioral patterns when the passwords were hidden, and many changed their behaviors significantly after the passwords were disclosed, suggesting their reported trust was influenced by their own judgments. Human-Generated and Machine-Generated Ratings of Password Strength: What Do Users Trust More? appeared on issue 21 of EAI endorsed transactions on Security and Safety journal.
5 Spill the Beans: Extrospection of Internet of Things by Exploiting Denial of Service
Internet of Things (exposes various vulnerabilities at different levels. One such exploitable vulnerability is Denial of Service (DoS). In this work, the authors focus on a large-scale extensive study of various forms of DoS and how it can be exploited in different protocols of IoT.
To understand how resilient is IoT for DoS, authors Vinay Sachidananda, Suhas Bhairav, and Yuval Elovici proposed two new metrics to measure the Resilience and the Quality of Service (QoS) degradation in IoT. They have conducted large-scale experimentation with real IoT devices in our security IoT testbed.
The experiments conducted are for DoS, Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) by setting up Mirai, and Permanent Denial of Service (PDoS) using BrickerBot on various IoT devices. They have also compared our framework with the existing state of the art tools. Spill the Beans: Extrospection of Internet of Things by Exploiting Denial of Service appeared on issue 20 of EAI endorsed transactions on Security and Safety journal.
Subscribe to our Security and Safety journal and never miss new content in your field of research.


